Lesson 2: ICD-10-PCS Sections Procedures in the Medical and Surgical Section Root Operation Groups Approaches Procedures in the Medical and Surgical-related Sections Obstetrics—Section 1 Placement—Section 2 Administration—Section 3 Measurement and Monitoring—Section 4 Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance—Section 5 Extracorporeal Therapies—Section 6 Osteopathic—Section 7 Other Procedures—Section 8 Chiropractic—Section 9 Procedures in the Ancillary Sections Imaging—Section B Nuclear Medicine—Section C Radiation Therapy—Section D Physical Rehabilitation and Diagnostic Audiology—Section F Mental Health—Section G Substance Abuse Treatment—Section New Technology–Section X Lesson 3: Coding in ICD-10-PCS ICD-10-PCS Coding – Key Concepts - Review Locating a Code in ICD-10-PCS Step-By-Step ICD-10-PCS Coding Examples ICD-10-PCS Learning Activity ICD-10-PCS Practice Questions Link to Post-Test
**************
Lesson 2: ICD-10-PCS Sections
Procedures in the Medical and Surgical section
This portion of the course provides reference material for the root operations in the Medical and Surgical section of ICD-10-PCS. The vast majority of codes reported in an inpatient setting are found in this section.Root Operation Groups
The Medical and Surgical root operations are divided into groups that share similar attributes.Root operations that take out some or all of a body part - Five root operations representing procedures for taking out or otherwise eradicating some or all of a body part are listed in the table below.
Root operations that take out solids/fluids/gases from a body part - Three root operations representing procedures that take out solids, fluids, or gases from a body part are listed in the table below.
Root operations involving cutting or separation only - Two root operations representing procedures that cut or separate a body part are listed in the table below.
Root operations that put in/put back or move some/all of a body part - Four root operations representing procedures that put in, put back, or move some or all of a body part are listed in the table below.
Root operations that alter the diameter/route of a tubular body part - Four root operations representing procedures that alter the diameter or route of a tubular body part are listed in table below.
Root operations that always involve a device - Six root operations representing procedures that always involve a device are listed in the table below.
Root operations involving examination only - Two root operations representing procedures that involve examination of a body part are listed in the table below.
Root operations that define other repairs - Two root operations representing procedures that define other repairs are listed in the table below.
The root operation REPAIR represents a broad range of procedures for restoring the anatomic structure of a body part such as suture of lacerations. REPAIR also functions as the “not elsewhere classified (NEC)” root operation, to be used when the procedure performed does not meet the definition of one of the other root operations.
Root operations that define other objectives - Three root operations in the Medical and Surgical section, FUSION, ALTERATION, and CREATION, describe procedures performed for three distinct reasons. Beyond that they have little in common.
A FUSION procedure puts a dysfunctional joint out of service rather than restoring function to the joint.
ALTERATION encompasses a whole range of procedures that share only the fact that they are done to improve the way the patient looks.
CREATION represents only two very specific sex change operations.
Approaches
The Medical and Surgical approaches used in root operations are listed in the table below.Procedures in the Medical and Surgical-related sections
Nine additional sections of ICD-10-PCS include procedures related to the Medical and Surgical section are listed in the table below.Obstetrics—Section 1
The OBSTETRICS section follows the same conventions established in the Medical and Surgical section, with all seven characters retaining the same meaning. There are twelve root operations in the OBSTETRICS section. Ten of these are also found in the Medical and Surgical section. Two root operations unique to OBSTETRICS are listed in the table below.Placement—Section 2
The PLACEMENT section follows the same conventions established in the Medical and Surgical section, with all seven characters retaining the same meaning. The root operations in the PLACEMENT section include only those procedures performed without making an incision or a puncture and are listed in the table below.Administration—Section 3
The ADMINISTRATION section includes infusions, injections, and transfusions, as well as other related procedures, such as irrigation and tattooing. All codes in this section define procedures where a diagnostic or therapeutic substance is given to the patient. Root operations in this section are classified according to the broad category of substance administered. If the substance given is a blood product or a cleansing substance, then the procedure is coded to TRANSFUSION and IRRIGATION respectively. All the other substances administered, such as anti-neoplastic substances, are coded to the root operation INTRODUCTION.Measurement and Monitoring—Section 4
There are two root operations in this section, and they differ in only one respect: MEASUREMENT defines one procedure and MONITORING defines a series of procedures. Instead of defining a device, the sixth character defines the physiological or physical function being tested.Extracorporeal or Systemic Assistance and Performance—Section 5
This section includes procedures performed in a critical care setting, such as mechanical ventilation and cardioversion. It also includes other procedures, such as hemodialysis and hyperbaric oxygen treatment. These procedures all use equipment to support a physiological function in some way, whether it is breathing, circulating the blood, or restoring the natural rhythm of the heart.The fifth and sixth characters in this section define duration and function respectively. These characters describe the duration of the procedure and the body function being acted upon, rather than the approach and device used.
The root operations ASSISTANCE and PERFORMANCE are two variations of the same kinds of procedures, varying only in the degree of control exercised over the physiological function.
EXTRACORPOREAL or SYSTEMIC THERAPIES—Section 6
Section 6 EXTRACORPOREAL or SYSTEMIC THERAPIES, describes other extracorporeal or systemic procedures that are not defined by ASSISTANCE and PERFORMANCE in Section 5 EXTRACORPOREAL or SYSTEMIC ASSISTANCE and PERFORMANCE. Examples are bili-lite phototherapy, apheresis, and whole body hypothermia.The second character contains a single general body system choice, PHYSIOLOGICAL SYSTEMS. The sixth character is defined as a qualifier, but contains no specific qualifier values. The seventh character qualifier identifies various blood components separated out in pheresis procedures.
The meaning of each root operation is consistent with the term as used in the medical community. DECOMPRESSION and HYPERTHERMIA have a more specialized meaning. All are defined in the table below.
Osteopathic—Section 7
Section 7, OSTEOPATHIC, is one of the smallest sections in ICD-10-PCS. There is a single body system, ANATOMICAL REGIONS, and a single root operation, TREATMENT.The sixth-character methods such as LYMPHATIC PUMP and FASCIAL RELEASE are not explicitly defined in ICD-10-PCS, and rely on the standard definitions as used in this specialty.
Other Procedures—Section 8
The OTHER PROCEDURES section contains codes for procedures not included in the other medical and surgical-related sections. A single root operation, OTHER PROCEDURES, is defined below.There are relatively few procedure codes in this section, for nontraditional, whole body therapies including acupuncture and meditation. There is also a code for the fertilization portion of an in-vitro fertilization procedure.
Chiropractic—Section 9
The CHIROPRACTIC section consists of a single body system, ANATOMICAL REGIONS, and a single root operation, MANIPULATION, defined below.Procedures in the Ancillary Sections
Six additional sections of ICD-10-PCS include procedures grouped in the ANCILLARY SECTIONS of ICD-10-PCS and are listed in the table below.Codes in these sections contain characters not previously defined, such as Contrast, Modality Qualifier and Equipment.
Imaging—Section B
IMAGING follows the same conventions established in the Medical and Surgical section for the section, body system, and body part characters. However, the third and fifth characters introduce definitions not used in previous sections.Third character defines procedure by root type, instead of root operation.
Fifth character defines contrast if used.
Sixth character is a qualifier that specifies an image taken without contrast followed by one with contrast.
Seventh character is a qualifier that is not specified in this section.
The IMAGING root types are defined in the following table:
Nuclear Medicine—Section C
NUCLEAR MEDICINE is organized like the IMAGING section. The only significant difference is that the fifth character defines the radionuclide instead of the contrast material used in the procedure.The third character classifies the procedure by root type instead of by root operation.
The fifth character specifies the radionuclide, the radiation source used in the procedure. Choices are applicable for the root procedure type.
The sixth and seventh characters are qualifiers, and are not specified in this section.
Radiation Therapy—Section D
RADIATION THERAPY contains the radiation procedures performed for cancer treatment. Character meanings are described below.Third character defines root type, which is the basic modality.
Fifth character further specifies treatment modality.
Sixth character defines the radioactive isotope used, if applicable.
Seventh character is a qualifier, and is not specified in this section.
The third character defines the treatment modality as root type. Examples are BRACHYTHERAPY and STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY. Four different root types are used in this section, as listed in the table below.
Physical Rehabilitation and Diagnostic Audiology—Section F
PHYSICAL REHABILITATION AND DIAGNOSTIC AUDIOLOGY contains character definitions unlike the other sections in ICD-10-PCS. They are described below.Second character is a section qualifier that specifies whether the procedure is a rehabilitation or diagnostic audiology procedure.
Third character defines the general procedure root type.
Fourth character defines the body system and body region combined, where applicable.
Fifth character further specifies the procedure type.
Sixth character specifies the equipment used, if any.
This section uses the third character to classify procedures into 14 root types. They are defined in the table below.
Mental Health—Section G
MENTAL HEALTH contains specific values in the third and fourth characters to describe mental health procedures. The remaining characters function as placeholders only. Character meanings are described below.Third character describes the mental health procedure root type.
Fourth character further specifies the procedure type as needed.
Second, fifth, sixth, and seventh characters do not convey specific information about the procedure. The value Z functions as a placeholder in these characters.
The third character describes the mental health root type. There are 11 root type values in this section, as listed in the table below.
SUBSTANCE ABUSE TREATMENT - SECTION H
SUBSTANCE ABUSE TREATMENT is structured like a smaller version of the MENTAL HEALTH section. Character meanings are described below.Third character describes the root type.
Fourth character is a qualifier that further classifies the root type.
Second, fifth, sixth, and seventh characters do not convey specific information about the procedure. The value Z functions as a placeholder in these characters.
There are seven different root type values classified in this section, as listed in the following table.
NEW TECHNOLOGY - SECTION X
Section X codes are standalone codes. They are not supplemental codes. Section X codes fully represent the specific procedure described in the code title, and do not require any additional codes from other sections of ICD-10-PCS. When section X contains a code title which describes a specific new technology procedure, only that X code is reported for the procedure. There is no need to report a broader, non-specific code in another section of ICD-10-PCS.Lesson 3: Coding in ICD-10-PCS
ICD-10-PCS - Key Concepts - Review
The ability of the coder to build the correct ICD-10-PCS code requires a greater knowledge of anatomy and physiology than under ICD-9-CM Volume 3. Furthermore, coders will continue to be dependent on physician documentation included in the operative or procedure reports.
ICD-10-PCS is used for facility reporting of hospital inpatient procedures and does NOT affect the use of CPT.
ICD-10-PCS is divided into Tables and an Index
The ICD-10-PCS Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting is a set of rules that go with the official conventions and instructions given within ICD-10-PCS
The ICD-10-PCS system structure is divided into 17 sections that name the general type of procedure or service.
Each ICD-10-PCS code character is an aspect of the procedure. Specify all 7 characters for a code to be valid.
The process of building an ICD-10-PCS code consists of assigning values from the valid choices for that part of the system using the rules for building codes.
ICD-10-PCS Tables give the available value choices to build a complete and valid code.
The ICD-10-PCS Index is an alphabetic lookup so you can locate the correct Table that has all the information you need to build a procedure code. It gives the first 3 or 4 values of the code and refers to a specific location in the Tables.
Section X, New Technology, provides a place for codes for certain new technology procedures not currently classified in ICD-10-PCS.
Proper procedure coding involves using the ICD-10-PCS to choose the correct codes for procedures or services based on documentation in a patient’s medical record and assigning those codes correctly on claims
The first character of an ICD-10-PCS code specifies the section
Characters 2-7 mean the same thing within each section, but may mean different things in other sections
In all sections, the third character specifies the general type of procedure performed
The purpose of the Index is to locate the correct Table that has all information needed to build a procedure code
The Index specifies the first 3 or 4 values of the code
Based on the first 3 values of the code in the Index, you can find the corresponding Table
Within an ICD-10-PCS Table, codes include all combinations of choices in characters 4-7 included in the same row of the Table
Common ICD-10 coding errors include: >Coding the diagnosis code and forgetting to code the procedure code >Coding the incorrect procedure code based on insufficient documentation in the medical record
If more than 1 procedure meets the definition of a principal procedure, list them on the claim and choose the 1 most related to the principal diagnosis as the principal procedure
With rare exceptions, ICD-10-PCS doesn't define multiple procedures with 1 code
...............
ICD-10-PCS Coding - Important Points
The ability of the coder to build the correct ICD-10-PCS code requires a greater knowledge of anatomy and physiology than under ICD-9-CM Volume 3. Furthermore, coders will continue to be dependent on physician documentation included in the operative or procedure reports.Locating a Code in ICD-10-PCS
Identify the main term(s) in the operative or procedure report, then reference in the Index.Review any subterms under the main term in the Index.
Follow any cross-reference instructions, such as –see, –see also.
Verify the code(s) selected from the Index in the Root Operation Tables.
All ICD-10-PCS codes consist of seven characters.
See the full text description for an ICD-10-PCS code in the List of Codes.
Example 1: Excision of chalazion from the left upper eyelid.
Example 2: Reattachment of right upper arm.
Example 3: Heart catheterization with cardiac mapping.
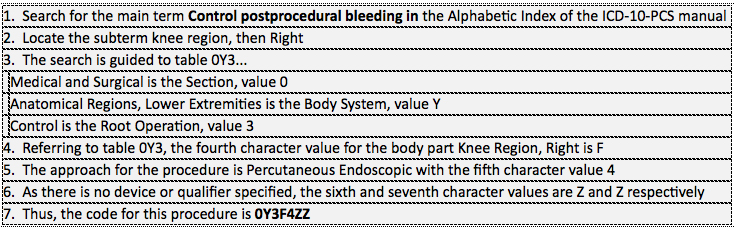
Example 4: Arthroscopy with drainage of hemarthrosis at previous operative site, right knee.
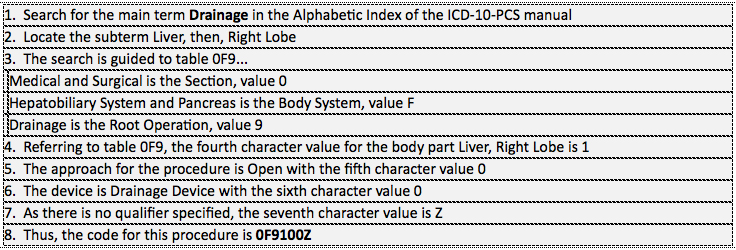
Example 5: Laparotomy with drain placement for liver abscess, right lobe.
Example 6: Replantation of avulsed scalp.
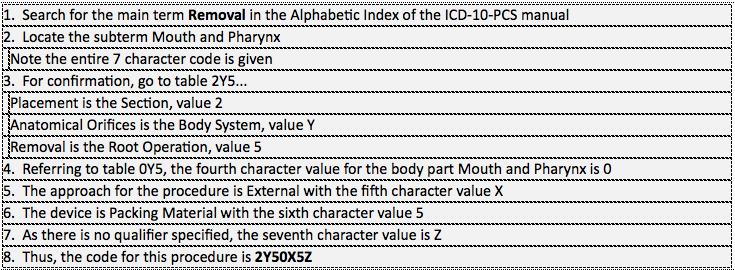
Example 7: Removal of packing material from pharynx.
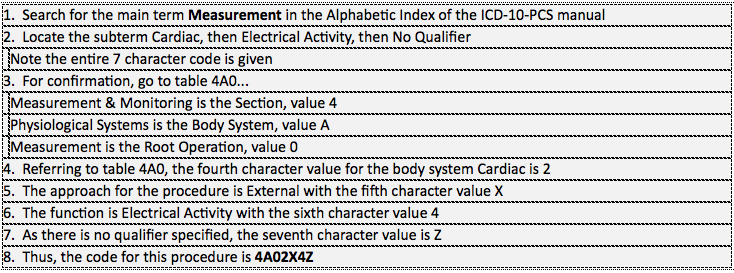
Example 8: External electrocardiogram (EKG), single reading.
Example 9: Ultraviolet light phototherapy, series treatment.
Example 10: X-ray of right clavicle, limited study.
|
• This activity will help assess your understanding of Root Operations and Approaches found in the ICD-10-PCS. (Click Check Answer: to reveal answer). Question #1 What is the root operation for post-prostatectomy bleeding? Question #2 What is the root operation for thrombectomy? Question #3 What is the root operation for herniorrhaphy? Question #4 Which approach is defined by procedures performed directly on the skin or mucous membrane and procedures performed indirectly by the application of external force through the skin or mucous membrane? Question #5 Which approach is defined by entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach and visualize the site of the procedure? Question #6 Which approach is defined by entry, by puncture or minor incision, through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach the site of the procedure? |
ICD-10-PCS Practice Questions
(Click "Check Answer" to reveal answer)...............
ICD-10-PCS Practice Question #1
One of ___ possible values can be assigned to each character in a code
- a) 14
- b) 24
- c) 34
- d) 44
...............
ICD-10-PCS Practice Question #2
A key feature of ICD-10-PCS is that information pertaining to a diagnosis is included from the code descriptions.
- True
- False
...............
ICD-10-PCS Practice Question #3
Which of the following is the first character/component of an ICD-10-PCS code?
- a) Root Operation
- b) Body System
- c) Section
- d) Approach
...............
ICD-10-PCS Practice Question #4
Imaging procedures, nuclear medicine, radiation oncology, physical rehab, diagnostic audiology, mental health and substance abuse treatment are collectively grouped into which section?
- a) Ancillary section
- b) Auxillary section
- c) Other procedures section
- d) Qualifiers section
...............
ICD-10-PCS Practice Question #5
What is the objective of root operation Destruction?
- a) Breaking solid matter into pieces.
- b) Cutting out/off without replacement.
- c) Eradicating without replacement.
- d) Pulling out or off without replacement.
...............
** Use the Index and Tables in your ICD10 PCS Manual (or online source) to answer the next questions **
ICD-10-PCS Practice Question #6
Which code is reported for Bypass Spinal Canal to Urinary Tract with Autologous Tissue Substitute, Percutaneous Approach?
- a) 00160J7
- b) 00163J7
- c) 00160J7
- d) 001U377
...............
ICD-10-PCS Practice Question #7
Which code is reported for Excision of Right External Iliac Artery, Percutaneous Endoscopic Approach, Diagnostic?
- a) 04BF4ZX
- b) 04BH4ZX
- c) 0410094
- d) 06BG4ZX
...............
ICD-10-PCS Practice Question #8
Which code is reported for Fluoroscopy of Right Tracheobronchial Tree using Other Contrast?
- a) BB27YZZ
- b) DB002ZZ
- c) BB09YZZ
- d) BB17YZZ
ICD-10-PCS Practice Question #9
Which code is reported for Respiratory Ventilation, Less than 24 Consecutive Hours?
- a) 5A1955Z
- b) 5A19054
- c) 5A1935Z
- d) 5A1945Z
...............
ICD-10-PCS Practice Question #10
Which code is reported for Postural Control Treatment of Integumentary System - Whole Body using Assistive, Adaptive, Supportive or Protective Equipment ?
- a) F0CH3UZ
- b) F0CH3FZ
- c) F0CH3EZ
- d) F0CH3UZ
...............
CLICK the link below to take the Post-Test for grading.
(Login using your first and last name and use the Password previously sent to you previously by e-mail)